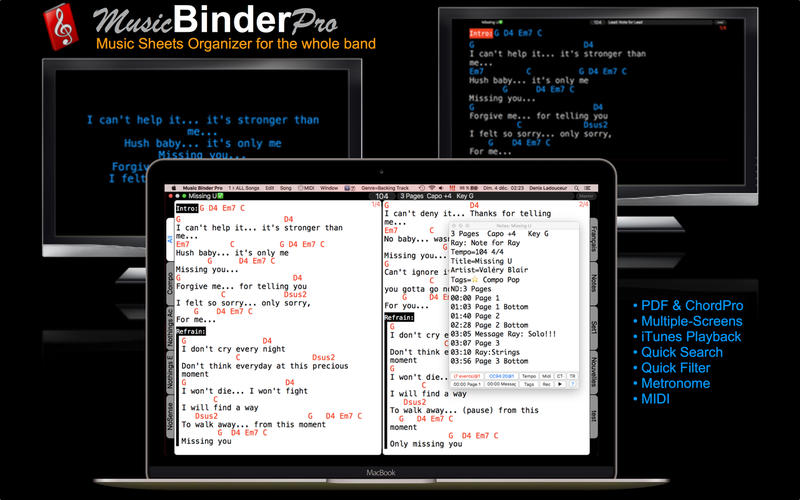
For string 6, this means that the pitch will change from 'low E' to 'high E.' If position 7 is pressed the string will be shortened to 2/3rds of its total length and the pitch will increase from 'low E' to 'B.' At position 5 the string will become 3/4ths of its total length and its pitch will increase from 'low E' to 'A.' 1.2 Pitch shifting: traditional methods 1.2.1 Shift the pitch up. To shift the pitch up, we usually use a capo to lock the strings at a specific spot on the neck. This reduces the length of each string and thus changes its fundamental frequency, which results in a new tuning at a higher pitch.
For string 6, this means that the pitch will change from 'low E' to 'high E.' If position 7 is pressed the string will be shortened to 2/3rds of its total length and the pitch will increase from 'low E' to 'B.' At position 5 the string will become 3/4ths of its total length and its pitch will increase from 'low E' to 'A.' 1.2 Pitch shifting: traditional methods 1.2.1 Shift the pitch up. To shift the pitch up, we usually use a capo to lock the strings at a specific spot on the neck. This reduces the length of each string and thus changes its fundamental frequency, which results in a new tuning at a higher pitch.
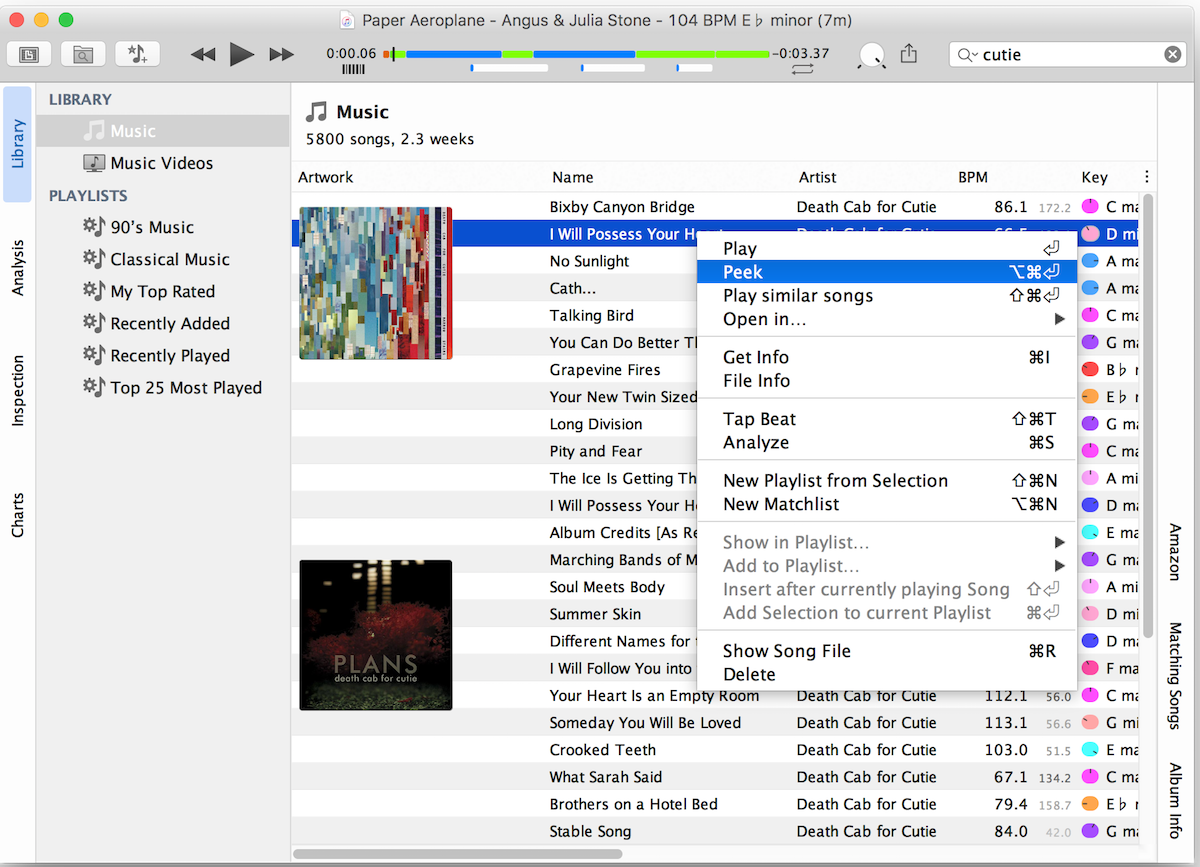
Stringed 2 8 – Shift Pitch And Manipulate Tempo Reale Tempo
The best pitch shifter pedal unlocks the range of your guitar, giving you access to a full gamut of intervals and octaves you couldn't otherwise naturally reach. Photomill 1 6 1. They do so intelligently, allowing you to dial in your key so you never inadvertently become ear-piercingly dissonant. Add onto or replace your original notes, the choice is yours..
FREQUENCY AND PITCH
After reading this section you will be able to do the following:
- Explain how you can change pitch by altering sources.
- Describe what resonance is.
Questions
- What happens when you make the string shorter? Longer? Thicker? Thinner? Tighter? Looser?
- What happens when you make the string out of different material?
Frequency and Resonance
Sound waves traveling through the air or other mediums sometimes affect the objects that they encounter. Recall that sound is caused by the molecules of a medium vibrating. Frequency refers to the number of vibrations that an individual particle makes in a specific period of time, usually a second. The frequency of a wave is different than the speed of a wave. Frequency refers to how often a wave passes through a certain point, while speed refers to how fast a wave passes through the point. Tooth fairy 2 4 3.
Particles vibrate at a specific frequency for each source, called its natural frequency. Steel, brass, and wood all have different natural frequencies. Occasionally, objects vibrating at their natural frequencies will cause resonance. Resonance is when objects with the same natural frequency as the vibrating source also begin to vibrate. Resonance does not happen very often and only affects object close to the vibrating source. Sometimes, the effects of resonance can be powerful. A singer can make glass vibrate enough to shatter, just by singing a note with the glass�s natural frequency!
Changing Pitch
Stringed 2 8 – Shift Pitch And Manipulate Tempo Reale Oggi
A string vibrates with a particular fundamental frequency. It is possible, however, to produce pitches with different frequencies from the same string. The four properties of the string that affect its frequency are length, diameter, tension, and density. These properties are described below:
Stringed 2 8 – Shift Pitch And Manipulate Tempo Reale E
- When the length of a string is changed, it will vibrate with a different frequency. Shorter strings have higher frequency and therefore higher pitch. When a musician presses her finger on a string, she shortens its length. The more fingers she adds to the string, the shorter she makes it, and the higher the pitch will be.
- Diameter is the thickness of the string. Thick strings with large diameters vibrate slower and have lower frequencies than thin ones. A thin string with a 10 millimeter diameter will have a frequency twice as high as one with a larger, 20 millimeter diameter. This means that the thin string will sound one octave above the thicker one.
- A string stretched between two points, such as on a stringed instrument, will have tension. Tension refers to how tightly the string is stretched. Tightening the string gives it a higher frequency while loosening it lowers the frequency. When string players tighten or loosen their strings, they are altering the pitches to make them in tune.
- The density of a string will also affect its frequency. Remember that dense molecules vibrate at slower speeds. The more dense the string is, the slower it will vibrate, and the lower its frequency will be. Instruments often have strings made of different materials. The strings used for low pitches will be made of a more dense material than the strings used for high pitches.